Executive Summary
The zLabs research team has identified a new threat campaign targeting Spanish Android users. DroidLock, a malware more accurately classified as ransomware, propagates via phishing websites. It has the ability to lock device screens with a ransomware-like overlay and illegally acquire app lock credentials, leading to a total takeover of the compromised device.
It employs deceptive system update screens to trick victims and can stream and remotely control devices via VNC. The malware also exploits device administrator privileges to lock or erase data, capture the victim's image with the front camera, and silence the device. Overall, it utilizes 15 distinct commands to interact with its C2 panel.
Technical Analysis
The infection starts with a dropper that deceives the user into installing the secondary payload that contains the actual malware (Figure 1). Using this technique the malware can bypass Android restriction to exploit Accessibility services.
Once the victim grants accessibility permission (Figure 2), the malware automatically approves additional permissions, such as those for accessing SMS, call logs, contacts, and audio.
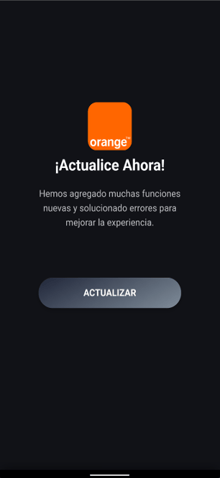
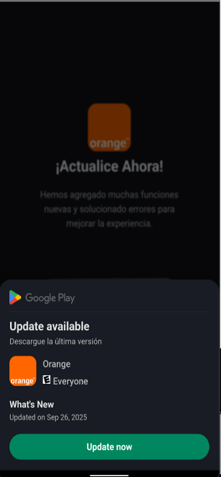
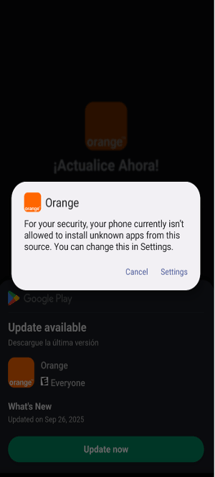
Fig. 1: Dropper installs the second stage
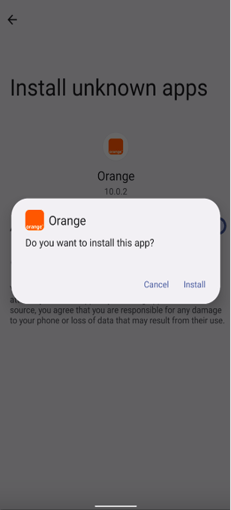

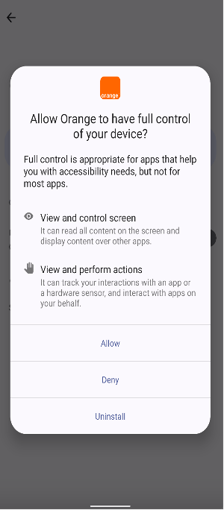
Fig. 2: Requesting accessibility services to perform fraud
C2 Communication
The malware leverages both websocket and HTTP communication in order to talk with its C2 (Command & Control server). In the first phase it uses the HTTP connection (Figure 3) to send basic information of the device for analytics. In a second phase, it uses websocket communication for receiving commands and sending data.
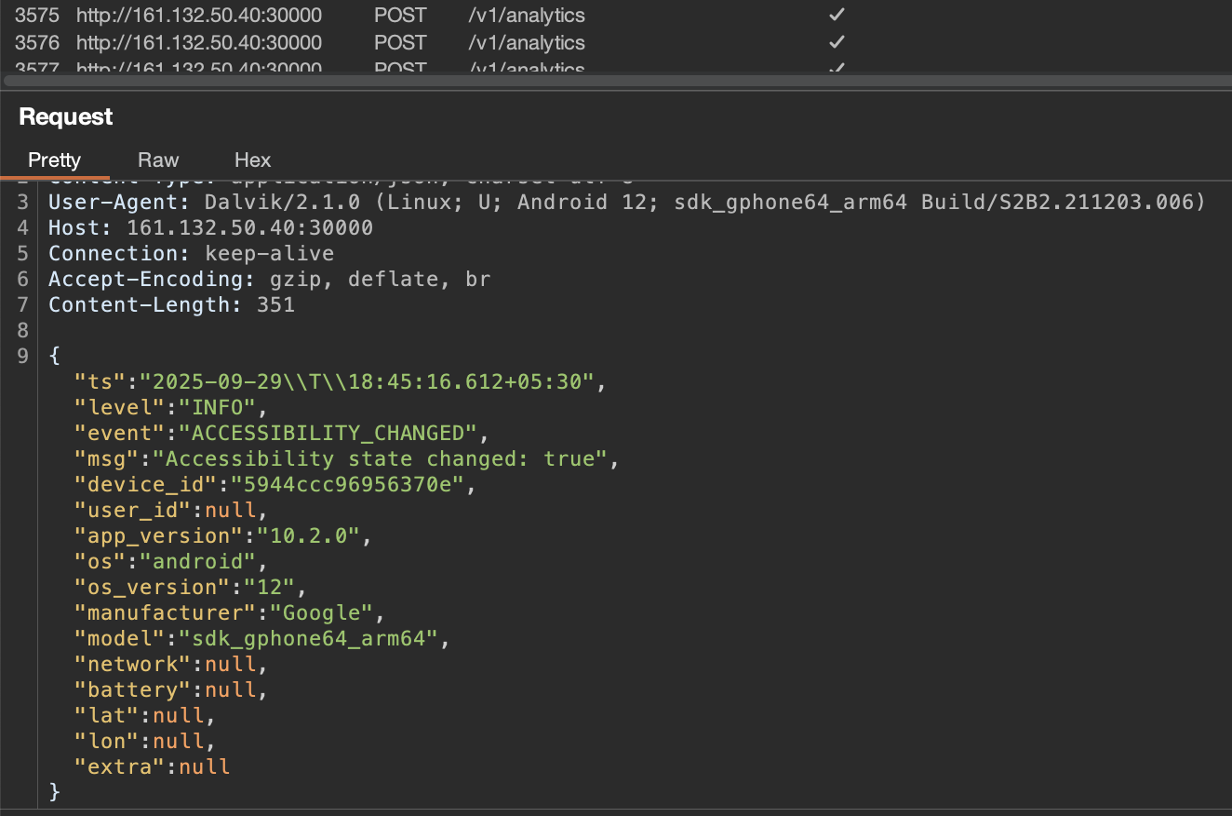
Fig. 3: Basic data sent to the server via http communication
Ransomware Capabilities
Scary Overlay
One of the malware’s capabilities include its ability to display a full screen overlay using webview on the victim's device upon receiving a Ransomware command from the C2. The overlay instructs immediate contact with the threat actor through email, requiring the device ID.
It issues a severe warning, failure to comply before 24 hours will result in the destruction of all files in the device. Unlike typical ransomware, this malware version does not actually encrypt files, however, it does have the capabilities to wipe the device entirely. Also, the full-screen warning (Figure 4) is highly alarming to the average internet user to pay the demanded ransom to the attacker.

Fig. 4: Ransomware style overly and admin contact details
Lock the User Out
The malware requests Device Admin Permission, along with the Accessibility Services Permission at the beginning of the installation. The malware uses this permission to have the ability to perform various fraudulent activities such as:
- Wiping data from the victim’s device, effectively performing a factory reset.
- Lock the device.
- Change the PIN, password or biometric information for preventing user’s access to the device.
Based on the command received from the C2 itself, the attacker can compromise the device indefinitely and lock the user out from accessing the device.
Accepted Commands
The malware maintains continuous communication with the C2 server while awaiting instructions from the threat actor. The analysis successfully identified all commands the malware accepts, which are detailed in the table below along with brief explanations.
| Command | Description |
| DEVICE_ADMIN | Requests device admin permission |
| BLACK_SCREEN | Black screen overlay on top of the screen |
| NOTIFICATION | Sends a notification with title, package name, and icon |
| BLOCK_BIOMETRIC | Locks the device using device admin privileges |
| BLACK_SCREEN_UPDATE_SYSTEM | Shows an update overlay and blocks user interactions |
| VNC | Sets the VNC flag to true |
| MUTE | Mutes the device |
| WIPE | Factory resets the device |
| RANSOMWARE | Shows a ransomware overlay |
| APP_BLOCK | Updates a stored list of blocked package names |
| APP_BLOCK_LOCK_PATTERN | Updates list of packages targeted for lock pattern theft |
| TURNSCREENON | Turns the screen on using a wakelock |
| CAMERA | Sets the camera flag to true |
| UNINSTALL_APP | Uninstalls a specific app received from the server |
| INJECT_APP | Overlays targeted app UI to steal credentials; stores overlays dynamically |
Dual Overlay Mechanisms for Credentials and Lock Pattern Theft
DroidLock malware leverages Accessibility Services to create overlays on targeted applications. When an AccessibilityEvent, specifically TYPE_WINDOW_STATE_CHANGED, originates from a package on the attacker's target list, the malware employs two primary overlay methods.
One method involves a fast, in-memory Lock Pattern overlay which is present in the assets folder of the APK. This presents a pattern-drawing UI to capture device unlock patterns (Figure.5). These overlay targets are managed by the APP_BLOCK_LOCK_PATTERN command, which includes targeted applications along with their package names and icons, all received from the server.
The second technique involves a WebView overlay. This overlay loads attacker-controlled HTML content stored locally in a database (Figure.6) that maps package names to their corresponding HTML. Whenever an application is opened, the malware queries the database for the specific package name. If a match is found it launches a full-screen WebView overlay that renders the stored HTML.
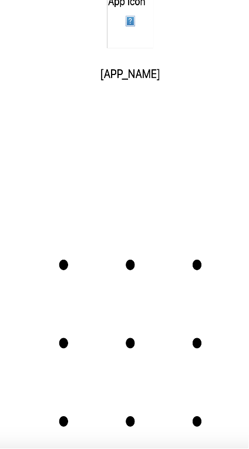
Fig. 5: Lock screen overlay placed on top of the screen
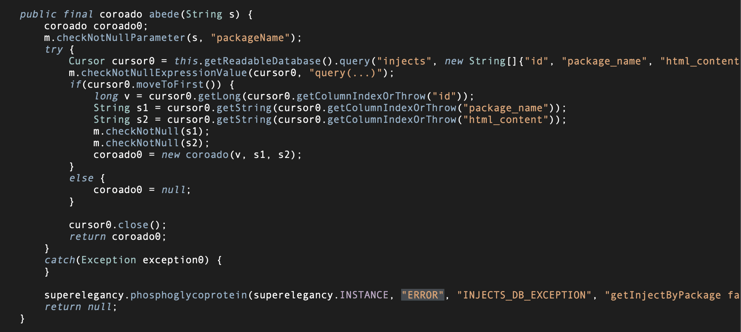
Fig. 6: Queries injections from the database
Keep the User Away
The malware employs a deceptive Android update screen (Figure 6), instructing victims not to power off or restart their devices. The overlay is put on top upon receiving the BLACK_SCREEN_UPDATE_SYSTEM command from the C2 server. This technique is commonly used by attackers to prevent user interaction while malicious activities are carried out in the background.
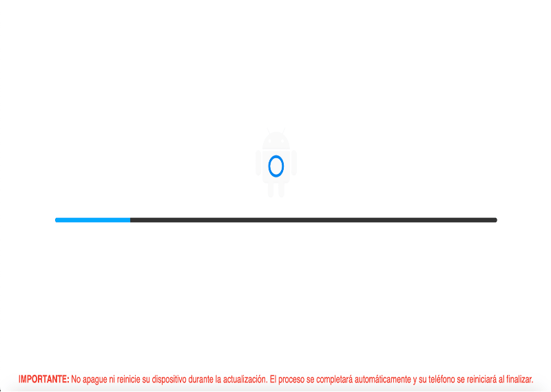
Fig. 6: Fake android update overlay
Screen Recording Feature
Another feature that the malware presents is the ability to secretly capture and transmit all screen activity to a remote server. It operates as a persistent foreground service, leveraging MediaProjection and VirtualDisplay to capture screen images.
These images are subsequently processed, converted to base64-encoded JPEG format, and dispatched to the server. This highly dangerous functionality could facilitate the theft of any sensitive information shown on the device’s display, including credentials, MFA codes, etc.
Zimperium vs DroidLock
Despite DroidLock’s wide range of takeover capabilities — including device-admin abuse, lock-screen manipulation, credential-stealing overlays, remote control, and full screen recording — Zimperium’s Mobile Threat Defense (MTD) and Mobile Application Runtime (zDefend) detect all found samples in a zero-day fashion using our on-device dynamic detection engine.
For enterprises, this matters. Once installed, DroidLock can wipe devices, change PINs, intercept OTPs, and remotely control the user interface, turning an infected phone into a hostile endpoint inside a corporate environment. Zimperium MTD provides protection even when devices are offline or operating outside managed networks, ensuring attacks like DroidLock are stopped before they lead to account compromise or operational disruption.
MITRE ATT&CK Techniques
| Tactic | ID | Name | Description |
| Initial Access | T1660 | Phishing | Adversaries host phishing websites to spread malicious Apk’s. |
| Persistence | T1624.001 | Event Triggered Execution: Broadcast Receivers | It creates a broadcast receiver to receive SMS events. |
| Privilege Escalation | T1626.001 | Abuse Elevation Control Mechanism: Device Administrator Permissions | Malware is capable of factory reset and disabling the lockscreen. |
| Defense Evasion | T1655.001 | Masquerading: Match Legitimate Name or Location | Malware pretending to be apps such as Orange. |
| Defense Evasion | T1629.002 | Device Lockout | Malware can lock out the victim through the device by using DevicePolicyManager.lockNow(). |
| Defense Evasion | T1516 | Input Injection | Malware can mimic user interaction, perform clicks and various gestures, and input data. |
| Credential Access | T1517 | Access Notifications | The malware leverages Android NotificationListenerService to intercept OTPs. |
| Credential Access | T1414 | Clipboard Data | It extracts data stored on the clipboard. |
| Credential Access | T1417.001 | Input Capture: Keylogging | It has a keylogger feature. |
| Credential Access | T1417.002 | Input Capture: GUI Input Capture | It is able to get the shown UI. |
| Discovery | T1430 | Location Tracking | Malware can track the victim's location. |
| Discovery | T1418 | Software Discovery | Malware collects installed application package list. |
| Discovery | T1426 | System Information Discovery | The malware collects basic device info. |
| Collection | T1517 | Access Notifications | It registers a receiver to monitor incoming SMS messages. |
| Collection | T1513 | Screen Capture | Malware can record screen content. |
| Collection | T1512 | Capture Camera | Malware opens camera and takes pictures. |
| Collection | T1429 | Audio Capture | Malware can mute the device. |
| Collection | T1636.004 | Protected User Data: SMS Messages | Steals SMSs from the infected device. |
| Collection | T1417.001 | Input Capture: Keylogging | Malware can capture keystrokes. |
| Collection | T1417.002 | Input Capture: GUI Input Capture | It is able to get the shown UI. |
| Collection | T1414 | Clipboard Data | It has the ability to steal data from the clipboard. |
| Command and Control | T1481.002 | Web Service: Bidirectional Communication | It uses websocket communication to poll the TA’s server and get the commands to execute. |
| Exfiltration | T1646 | Exfiltration Over C2 Channel | Sending exfiltrated data over the C&C server. |
| Impact | T1516 | Input Injection | It displays injected payloads like pattern locks and mimics banking app login screens through overlay to steal credentials. |
| Impact | T1582 | SMS Control | It can read and send SMS. |
Indicators of Compromise
The full list of IOCs can be found in this repository.


